Information
INR/SNR
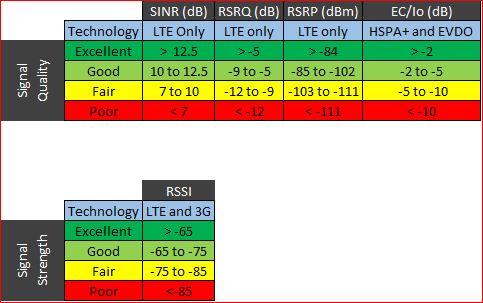
The signal-to-noise ratio of the given signal.RSRP
Reference Signals Received Power is a measurement of the received power level in an LTE cell network. The average power received from a single Reference signal, and Its typical range is around -44dbm (good) to -140dbm(bad).RSRQ
Reference Signal Received Quality - Indicates quality of the received signal, and its range is typically -19.5dB(bad) to -3dB (good).RSSI
Received Signal Strength Indicator: Represents the entire received power including the wanted power from the serving cell as well as all cochannel power and other sources of noise and it is related to the above parameters through the following formula: RSSI for LTE is a calculated from several other signal related measurements: RSSI = wideband power = noise + serving cell power + interference power. For example, a 4G LTE modem might report an RSSI of -68 dBm, but: RSRP = -102 dBm RSRQ = -16 dB SINR = -1.8 dB In this case, the signal quality is actually very poor. This could be due to the device being some distance away from the LTE transmitter. It’s also possible that something is interfering with the signal, such as a building or other obstructions between the device and the tower.CID
A GSM Cell ID (CID) is a generally unique number used to identify each base transceiver station (BTS) or sector of a BTS within a location area code (LAC) if not within a GSM network.Operating Band
(indicated as ABND on the Squid) is the operating band of the transmission.The Determining Factors of Signal Values
There are many different factors that influence signal strength and quality, including but not limited to:- Proximity to the cellular tower
- Tower load
- Physical barriers (mountains, buildings, trains, etc.)
- Competing signals
- Weather
- Signal going through a cellular repeater
Noise Floor
is the signal created from adding up all the unwanted signals within a measurement system. The noise floor consists of noise from a number of sources which includes thermal noise, atmospheric noise and noise from components used to make the measurement system.Noise floor is an important parameter in spectrum analyzers and vector network analyzers. It determines the lowest possible signal level that these systems can measure. For example, to measure a signal that is -140 dBm, the system must have a noise floor of less than -140 dBm.
In Spectrum Analyzers and VNAs the Noise Floor is called the Displayed Average Noise Level (DANL).
Equipment Information
[Import from ERP] /erp/asset/ItemData Capture Options (9-14-2019)
